Technical News
Tips for Selecting Diesel Engine Cylinder Heads
Selecting the correct cylinder head for a diesel engine is crucial to optimizing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reliability. Diesel engines are primarily used in heavy-duty equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, loaders, trucks, and other commercial and industrial machinery. Here are some essential tips for choosing the right diesel engine cylinder head for your application, whether for commercial, off-road, or industrial use.

1. Understand Your Engine Model and Application
The first step in selecting a diesel engine cylinder head is to determine the engine model and its specific application. Diesel engines vary widely depending on their use in heavy-duty machinery. It is essential to choose a cylinder head that matches both the engine model (e.g., CAT C9, Cummins 6.7L) and the specific requirements of the application, such as:
- Excavators and Bulldozers: These require durable, high-torque engines for heavy lifting and digging tasks.
- Trucks and Commercial Vehicles: These engines must perform efficiently over long hours, often with a focus on fuel economy and reliability.
- Loaders and Industrial Machines: Engines must handle heavy loads and demanding work environments.
Ensure the cylinder head matches the engine's requirements based on the application, whether it is for construction, mining, or transportation.

2. Prioritize Durability and Material Quality
In diesel engines, especially those used in heavy-duty equipment, cylinder heads are subjected to extreme heat, pressure, and mechanical stress. Material quality is critical to ensure the longevity and reliability of the engine. Diesel engine cylinder heads are typically made from:
Aluminum Alloy: Lighter than cast iron, aluminum alloy offers better heat dissipation. However, for heavy-duty equipment, cast iron is generally preferred due to its superior durability under high stress.e aluminum alloy heads may be preferred for more modern, performance-oriented engines.
Cast Iron: Known for its strength and ability to withstand high temperatures, cast iron is ideal for heavy-duty diesel engines, as it offers excellent wear resistance and can handle the high cylinder pressures in industrial and commercial applications.
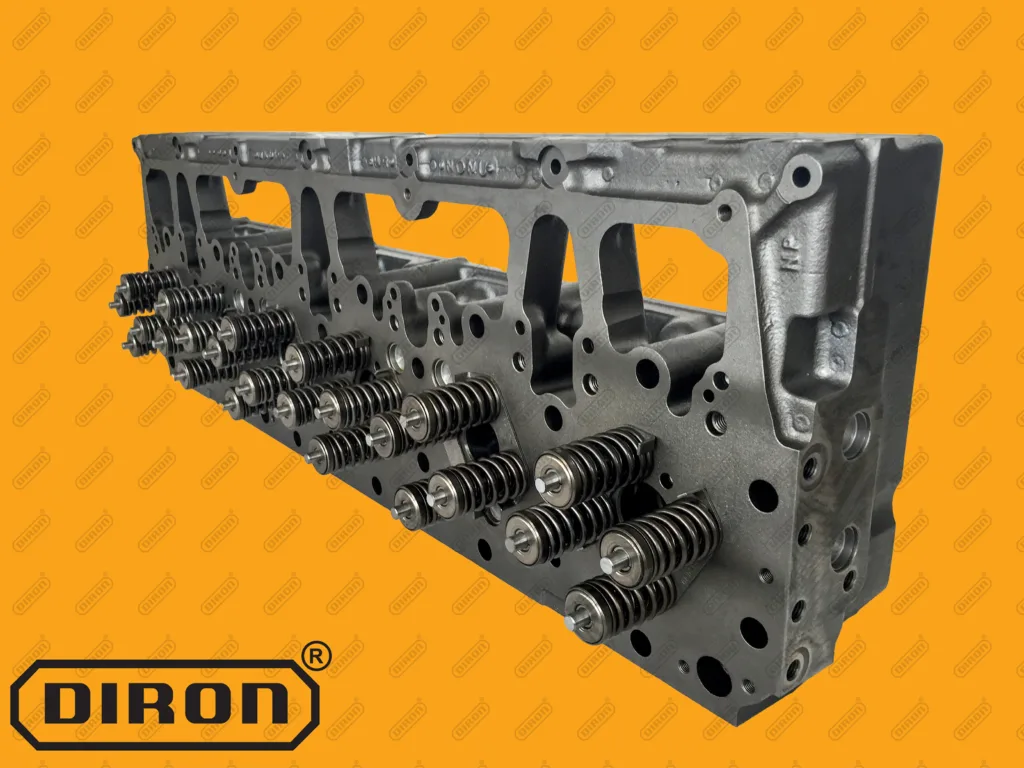

3. Match Cylinder Head Design to the Engine’s Needs
Cylinder head design plays a significant role in engine performance, especially in diesel applications where combustion efficiency and power delivery are critical. Key design factors to consider include:
- Valve Configuration: Diesel engines typically feature multiple valves per cylinder to optimize airflow and combustion. Ensure the cylinder head matches the engine's valve configuration.
- Port Design and Size: Larger intake ports may be needed for performance-oriented applications, while smaller ports may be better suited for engines that focus on low-end torque and fuel efficiency.
- Combustion Chamber Design: The chamber's shape impacts the engine’s compression ratio, fuel efficiency, and overall power output. Choose a cylinder head that supports the specific needs of your application.
4. Consider the Role of Turbocharging and Boosted Applications
For many modern diesel engines, turbocharging is a critical feature that enhances performance. Turbocharged engines require cylinder heads that can withstand the high pressures generated by forced induction. In such cases:
- Stronger Casting Materials: Ensure the cylinder head is made from robust materials or designed with additional reinforcement to handle higher cylinder pressures.
- Upgraded Valve Materials: Turbocharged engines often require Inconel valves for exhaust components to withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures.
- Heavy-Duty Valve Springs: Diesel engines with turbochargers often need upgraded valve springs to handle the increased pressure and maintain valve control.
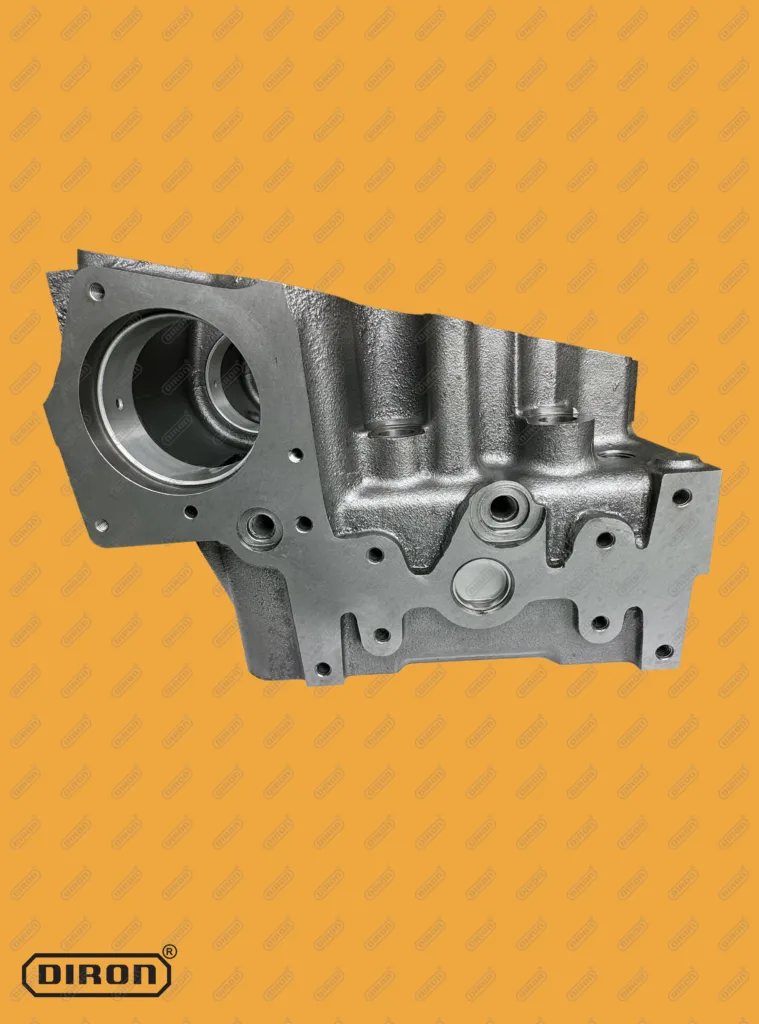

5. Match Cylinder Head Runner Volume to Application
The runner volume of the cylinder head affects engine airflow and performance. Diesel engines require a balance between low-end torque for heavy-duty tasks and high-flow capabilities for optimal fuel efficiency. Key considerations include:
- Larger Runners: Suitable for engines that need higher power output, such as larger commercial trucks or industrial equipment.
- Smaller Runners: Better suited for applications that prioritize fuel efficiency and torque, such as smaller off-road machinery or vehicles used for long-haul transport.
Choose the runner volume based on your engine's rpm range and the specific requirements of your application.
6. Assess Cylinder Head Flow and Efficiency
Flow characteristics of the cylinder head, particularly at partial valve lift, are vital for ensuring good performance at lower and mid-range rpm, where most diesel engines operate. Focus on:
- Flow at Partial Lift: Diesel engines typically run at lower rpm than gasoline engines, so it's important that the cylinder head maintains good airflow even at partial valve lift.
- Peak Flow: While peak flow numbers are important, the real-world performance of the engine will depend more on how well the cylinder head flows at lower rpm and during the transition from low to high revs.
Using a flow bench to evaluate cylinder head performance is an excellent way to compare different options.cant low-end torque.
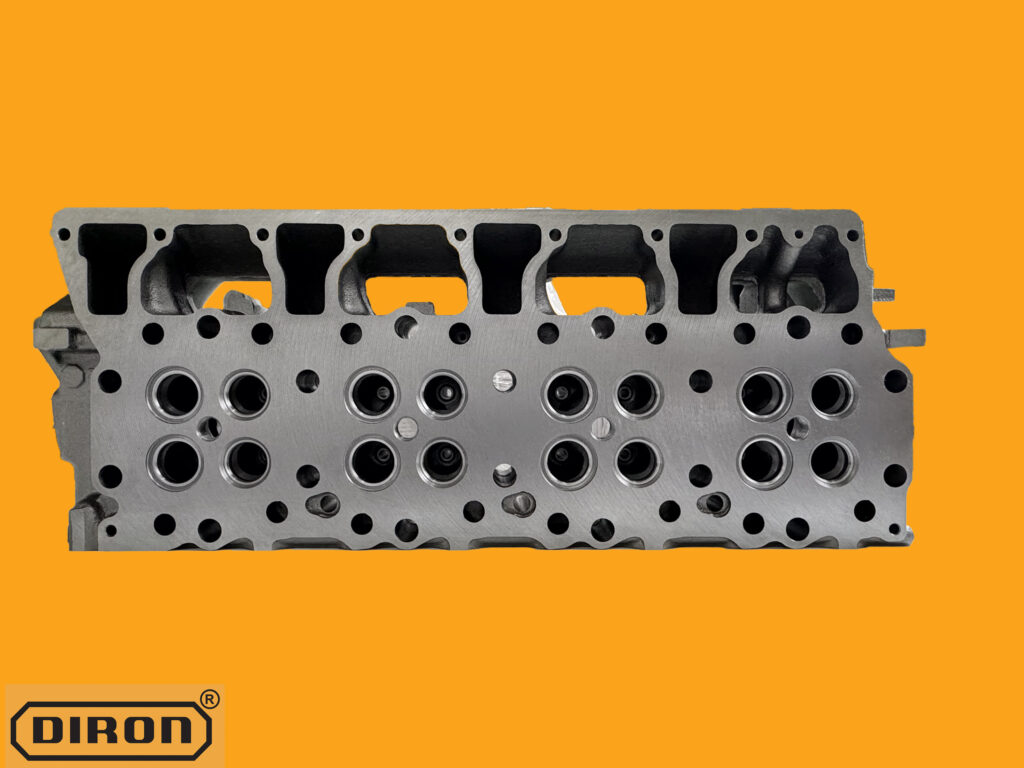

7. Review Budget and Customer Requirements
The budget is always a significant factor when selecting a cylinder head. While high-performance, CNC-ported heads offer superior flow and performance, they come at a higher price. For heavy-duty machinery applications, you should balance:
- Cost vs. Performance: Consider whether the customer requires a high-end, performance-oriented cylinder head or a more cost-effective solution that still offers reliability and durability.
- Specific Application Needs: For example, an excavator engine may not require the same high-performance head as a truck engine used for long-distance hauling. Focus on meeting the application’s needs while staying within budget.
8. Warranty and After-Sales Support
Cylinder heads are significant investments, so it is essential to ensure a warranty and after-sales support. Many suppliers offer warranties, and some even provide extended support for maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Warranty: Make sure the cylinder head comes with a reasonable warranty, particularly for heavy-duty or industrial applications where engine downtime is costly.
- Technical Support: In case of issues during installation or maintenance, ensure that the manufacturer or supplier offers robust technical support.
A cylinder head is just one component of a complex engine system. Ensure compatibility with other engine components, including:
- Fuel System: Depending on the type of diesel engine, fuel system modifications may be necessary to handle the higher fuel flow associated with a high-flow cylinder head.
- Turbocharger and Exhaust System: Ensure the cylinder head works in harmony with the turbocharger and exhaust systems, especially in turbocharged applications.

Conclusion
Selecting the right diesel engine cylinder head is essential for optimizing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and durability. By considering factors such as material quality, design, turbocharging requirements, and customer needs, you can choose the best cylinder head for your diesel engine, whether it's for heavy-duty machinery, commercial trucks, or off-road equipment.

